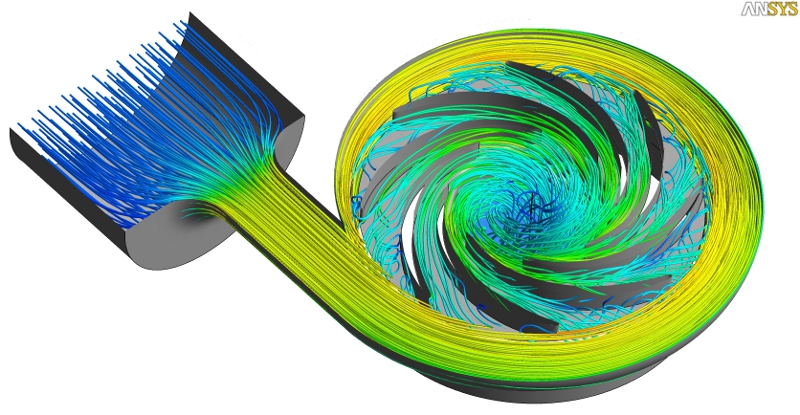
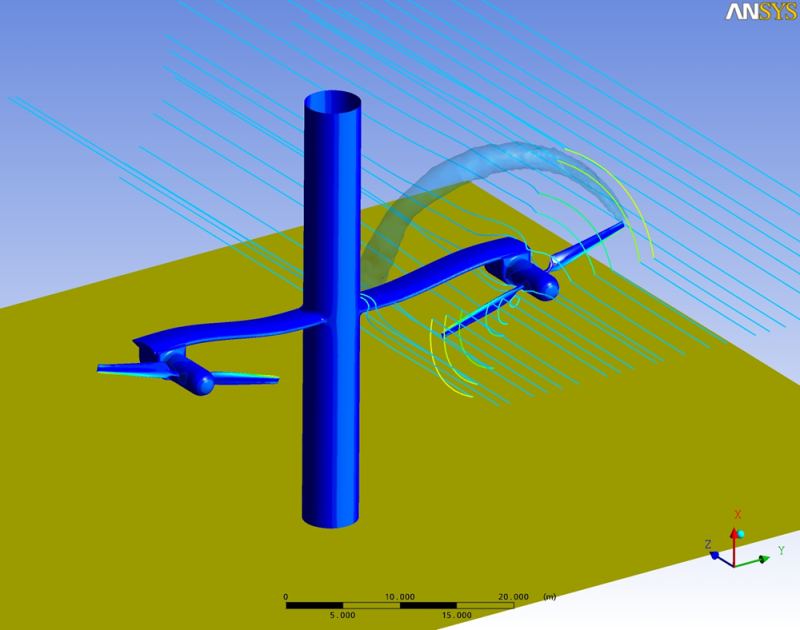
CFD Applications
|
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is an area of fluid mechanics, based on numerical methods and algorithms for solving problems that involve fluid flows. Engineers are using computers to simulate the behavior of fluids by solving the equations of continuity and momentum (Navier-Stokes equations) in conjunction with the equation of mass and energy conservation, having the geometry and boundary conditions defined by the user. It is an effective and handy engineering tool and can be used to study the effect of various parameters (geometry, fluid properties, boundary conditions, etc.) on flow characteristics (velocity distribution, pressure drop, heat/mass transfer, etc.). |
some images displayed on this page are property of ANSYS Inc. and are used here for promotion only. |
||||||||
|
To solve a physical problem using CFD, the basic steps are:
Results can be presented in terms of flow characteristics (eg speed, pressure, shear stress) in various figure types (eg contours, iso-, streamlines, etc.), either as an animation. In our Laboratory, we are working on the study and design of efficient process equipment using the commercial codes ANSYS CFX και FLUENT. |
|
||||||||
|
Wavy Stratified Gas-Liquid Flow. |
|
| » | Study of flooding mechanism in vertical small diameter pipes. |
| » | Study and optimization of a compact heat exchanger |
| » | Transport phenomena in narrow channels with corrugated walls |
| » | Study of a bubble column reactor |
| » | Study of bubble genesis (work in progress) |